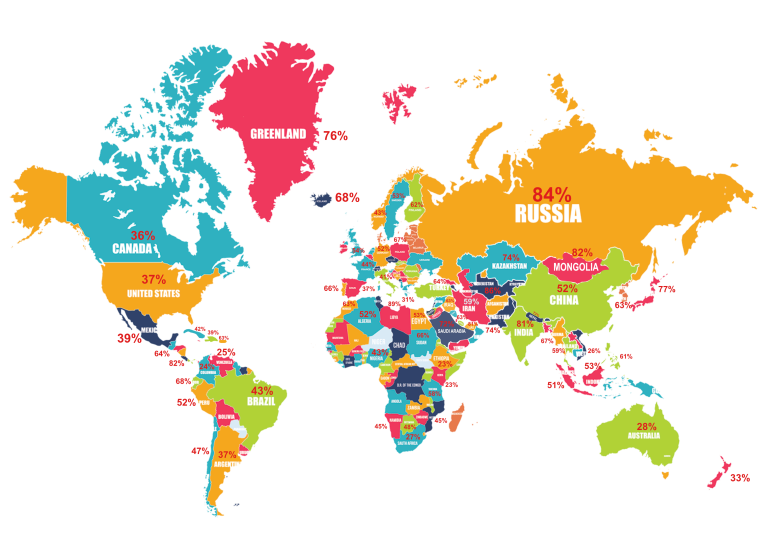
Why it’s a global problem
Widespread prevalence: The deficiency is widespread across the world, affecting all age groups, according to ScienceDirect and the National Institutes of Health.
Contributes to disease burden: Its high prevalence would increase the global burden of disease, making prevention a public health priority, notes the National Institutes of Health.
Health impacts: It is associated with numerous health issues beyond bone problems, including infectious diseases (like severe COVID-19 and upper respiratory infections), muscle weakness, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease.
Data gaps: Despite the evidence, many countries lack sufficient data on vitamin D status, particularly for vulnerable groups like infants, children, adolescents, and pregnant women.
Risk factors: Risk factors for deficiency include air pollution, lack of sun exposure due to lifestyle or location, and certain diets.

WhatsApp us